Spotlight
A selection of stories from across the Federation

Advances in Sexual and Reproductive Rights and Health: 2024 in Review
Let’s take a leap back in time to the beginning of 2024: In twelve months, what victories has our movement managed to secure in the face of growing opposition and the rise of the far right? These victories for sexual and reproductive rights and health are the result of relentless grassroots work and advocacy by our Member Associations, in partnership with community organizations, allied politicians, and the mobilization of public opinion.
Most Popular This Week
Brazil, Czech Republic, Japan, Estonia, Namibia, Nepal, Thailand

The Rainbow Wave for Marriage Equality
Love wins! The fight for marriage equality has seen incredible progress worldwide, with a recent surge in legalizations.

Advances in Sexual and Reproductive Rights and Health: 2024 in Review
Let’s take a leap back in time to the beginning of 2024: In twelve months, what victories has our movement managed to secure in t
Kazakhstan
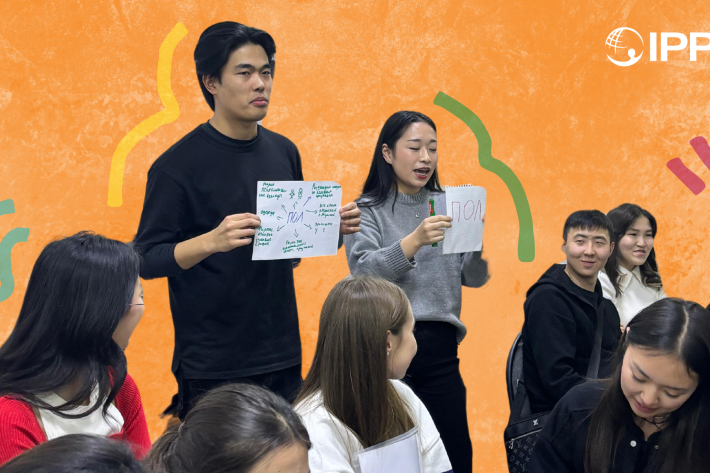

Kazakhstan's Rising HIV Crisis: A Call for Action
On World AIDS Day, we commemorate the remarkable achievements of IPPF Member Associations in their unwavering commitment to combating the HIV epidemic.

Ensuring SRHR in Humanitarian Crises: What You Need to Know
Over the past two decades, global forced displacement has consistently increased, affecting an estimated 114 million people as of mid-2023.
France, Germany, Poland, United Kingdom, United States, Colombia, India, Tunisia

Abortion Rights: Latest Decisions and Developments around the World
Over the past 30 years, more than

Palestine
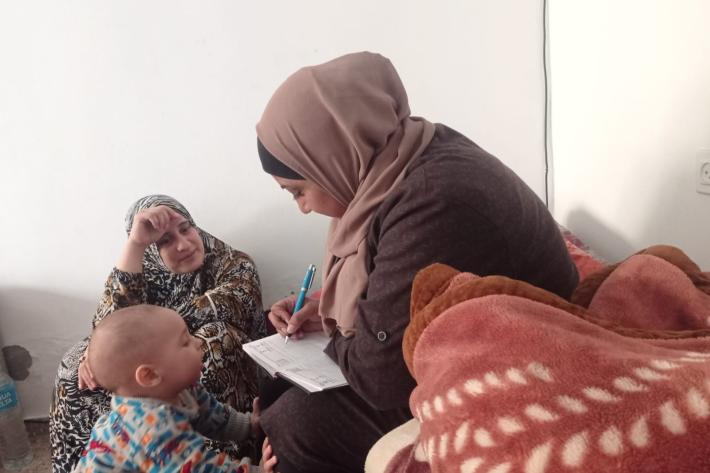

In their own words: The people providing sexual and reproductive health care under bombardment in Gaza
Week after week, heavy Israeli bombardment from air, land, and sea, has continued across most of the Gaza Strip.
Vanuatu
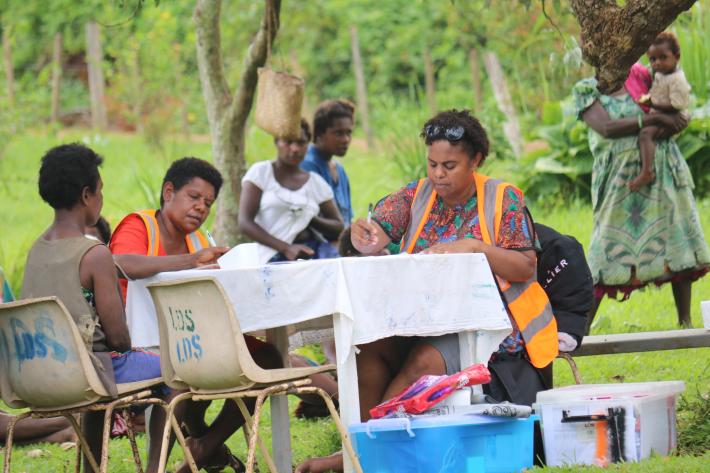

When getting to the hospital is difficult, Vanuatu mobile outreach can save lives
In the mountains of Kumera on Tanna Island, Vanuatu, the village women of Kamahaul normally spend over 10,000 Vatu ($83 USD) to travel to the nearest hospital.
Filter our stories by:


| 16 August 2018
Inspiring young people like Chathurika play a crucial role in crisis response
In May 2017, flash flooding in Sri Lanka triggered landslides resulting in many people losing their homes, forcing them to seek shelter in camps. IPPF’s member association the Family Planning Association of Sri Lanka (FPASL) assisted those affected and provided health camps with the support of IPPF Humanitarian. Chathurika Jayalath, a youth volunteer for FPASL, took part in the response. Chathurika is a 24-year-old student from Kegalle, a large town about 80 km from Colombo, and she has been working with FPASL for the last three years. She started out as a youth volunteer and recently became a member of the Youth Technical Advisory Committee. During her engagement with FPASL, Chathurika has learned about sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) and gender issues and has organized workshops on similar topics in her own community. In fact, she runs a youth club at her university to inform her peers about SRHR. Shortly after the floods began, Chathurika received a WhatsApp message from FPASL where they called for youth volunteers to take part in the response. “I wanted to volunteer during the response,” Chathurika told us. “As a university student I didn’t have money to donate so I figured I could contribute with my strength instead. I volunteered in the health camp. There, I assisted the medical staff with basic things such mobilizing affected people, making sure they queued up when seeking health care and packed medicine.” Ongoing SRHR needs, even in a crisis Chathurika is keen to learn more about humanitarian work. She received training with FPASL on the needs of people in humanitarian settings in which she and other trainees were presented with different case studies. “There was particularly one story that struck me. We were told that when the flash floods came, women fled without anything, they fled with the only pair of clothes they were wearing,” recalls Chathurika. “When they reached the camp, they received donated water and food. Some of them got their period while living in the camp. They did not have any sanitary pads nor additional cloths. Some of them even fled without underwear. This story made me realize that people’s SRHR needs don’t disappear just because there is a crisis.” Youth empowerment is important to Chathurika and she would like to continue this work while learning more about development and humanitarian work. She is a firm believer “that young people can contribute. Through my own experience I have seen that it is possible.”

| 15 February 2026
Inspiring young people like Chathurika play a crucial role in crisis response
In May 2017, flash flooding in Sri Lanka triggered landslides resulting in many people losing their homes, forcing them to seek shelter in camps. IPPF’s member association the Family Planning Association of Sri Lanka (FPASL) assisted those affected and provided health camps with the support of IPPF Humanitarian. Chathurika Jayalath, a youth volunteer for FPASL, took part in the response. Chathurika is a 24-year-old student from Kegalle, a large town about 80 km from Colombo, and she has been working with FPASL for the last three years. She started out as a youth volunteer and recently became a member of the Youth Technical Advisory Committee. During her engagement with FPASL, Chathurika has learned about sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) and gender issues and has organized workshops on similar topics in her own community. In fact, she runs a youth club at her university to inform her peers about SRHR. Shortly after the floods began, Chathurika received a WhatsApp message from FPASL where they called for youth volunteers to take part in the response. “I wanted to volunteer during the response,” Chathurika told us. “As a university student I didn’t have money to donate so I figured I could contribute with my strength instead. I volunteered in the health camp. There, I assisted the medical staff with basic things such mobilizing affected people, making sure they queued up when seeking health care and packed medicine.” Ongoing SRHR needs, even in a crisis Chathurika is keen to learn more about humanitarian work. She received training with FPASL on the needs of people in humanitarian settings in which she and other trainees were presented with different case studies. “There was particularly one story that struck me. We were told that when the flash floods came, women fled without anything, they fled with the only pair of clothes they were wearing,” recalls Chathurika. “When they reached the camp, they received donated water and food. Some of them got their period while living in the camp. They did not have any sanitary pads nor additional cloths. Some of them even fled without underwear. This story made me realize that people’s SRHR needs don’t disappear just because there is a crisis.” Youth empowerment is important to Chathurika and she would like to continue this work while learning more about development and humanitarian work. She is a firm believer “that young people can contribute. Through my own experience I have seen that it is possible.”

| 08 February 2018
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 15 February 2026
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”
| 08 February 2018
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 15 February 2026
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 08 February 2018
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 15 February 2026
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 16 August 2018
Inspiring young people like Chathurika play a crucial role in crisis response
In May 2017, flash flooding in Sri Lanka triggered landslides resulting in many people losing their homes, forcing them to seek shelter in camps. IPPF’s member association the Family Planning Association of Sri Lanka (FPASL) assisted those affected and provided health camps with the support of IPPF Humanitarian. Chathurika Jayalath, a youth volunteer for FPASL, took part in the response. Chathurika is a 24-year-old student from Kegalle, a large town about 80 km from Colombo, and she has been working with FPASL for the last three years. She started out as a youth volunteer and recently became a member of the Youth Technical Advisory Committee. During her engagement with FPASL, Chathurika has learned about sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) and gender issues and has organized workshops on similar topics in her own community. In fact, she runs a youth club at her university to inform her peers about SRHR. Shortly after the floods began, Chathurika received a WhatsApp message from FPASL where they called for youth volunteers to take part in the response. “I wanted to volunteer during the response,” Chathurika told us. “As a university student I didn’t have money to donate so I figured I could contribute with my strength instead. I volunteered in the health camp. There, I assisted the medical staff with basic things such mobilizing affected people, making sure they queued up when seeking health care and packed medicine.” Ongoing SRHR needs, even in a crisis Chathurika is keen to learn more about humanitarian work. She received training with FPASL on the needs of people in humanitarian settings in which she and other trainees were presented with different case studies. “There was particularly one story that struck me. We were told that when the flash floods came, women fled without anything, they fled with the only pair of clothes they were wearing,” recalls Chathurika. “When they reached the camp, they received donated water and food. Some of them got their period while living in the camp. They did not have any sanitary pads nor additional cloths. Some of them even fled without underwear. This story made me realize that people’s SRHR needs don’t disappear just because there is a crisis.” Youth empowerment is important to Chathurika and she would like to continue this work while learning more about development and humanitarian work. She is a firm believer “that young people can contribute. Through my own experience I have seen that it is possible.”

| 15 February 2026
Inspiring young people like Chathurika play a crucial role in crisis response
In May 2017, flash flooding in Sri Lanka triggered landslides resulting in many people losing their homes, forcing them to seek shelter in camps. IPPF’s member association the Family Planning Association of Sri Lanka (FPASL) assisted those affected and provided health camps with the support of IPPF Humanitarian. Chathurika Jayalath, a youth volunteer for FPASL, took part in the response. Chathurika is a 24-year-old student from Kegalle, a large town about 80 km from Colombo, and she has been working with FPASL for the last three years. She started out as a youth volunteer and recently became a member of the Youth Technical Advisory Committee. During her engagement with FPASL, Chathurika has learned about sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) and gender issues and has organized workshops on similar topics in her own community. In fact, she runs a youth club at her university to inform her peers about SRHR. Shortly after the floods began, Chathurika received a WhatsApp message from FPASL where they called for youth volunteers to take part in the response. “I wanted to volunteer during the response,” Chathurika told us. “As a university student I didn’t have money to donate so I figured I could contribute with my strength instead. I volunteered in the health camp. There, I assisted the medical staff with basic things such mobilizing affected people, making sure they queued up when seeking health care and packed medicine.” Ongoing SRHR needs, even in a crisis Chathurika is keen to learn more about humanitarian work. She received training with FPASL on the needs of people in humanitarian settings in which she and other trainees were presented with different case studies. “There was particularly one story that struck me. We were told that when the flash floods came, women fled without anything, they fled with the only pair of clothes they were wearing,” recalls Chathurika. “When they reached the camp, they received donated water and food. Some of them got their period while living in the camp. They did not have any sanitary pads nor additional cloths. Some of them even fled without underwear. This story made me realize that people’s SRHR needs don’t disappear just because there is a crisis.” Youth empowerment is important to Chathurika and she would like to continue this work while learning more about development and humanitarian work. She is a firm believer “that young people can contribute. Through my own experience I have seen that it is possible.”

| 08 February 2018
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 15 February 2026
"...now I can provide MR (menstrual regulation) services efficiently."
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Nursing Supervisor Ms. Lovely Yasmin is one of several staff members providing family planning, menstrual regulation, and post-procedure care services at Upzila Health Complex in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. “Before this training we used to sometimes advise people on such services and provided menstrual regulation (MR) services but after the training I’ve have become and confident and efficient in providing MR services,” she says. “Earlier there could possibly have been mistake but now I can provide MR services efficiently and perfectly. I can now provide MR services in more organized manner.” But while Yasmin, who has worked in family planning for 16 years, says that the recent training has increased her confidence in properly doing MR procedures, the health complex still lacks basic supplies. “There were difficulties due to limited equipment,” she says. “We sometimes have to use personal equipment.” But, she says, the presence of Kit 8 has made life easier. “Prior to this kit, many clients did not complete the full course of medical as advices due to financial issues… during floods there are many hardships including financial difficulty,” she says. “However with this kit, most of the medicines are provided and clients are easily managing on their own.”

| 08 February 2018
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 15 February 2026
“After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. When Shana Khatun, a mother of three, became pregnant again she says she began to feel very weak and had issues with massive bleeding.Citing her age and the possibility of further medical complications, Khatun decided to undergo a menstrual regulation procedure. “But if the hospital and services weren’t there then I would have had to have continued with my pregnancy, even when (I do) not want another child” she says. Khatun says that the procedure went well, but that without the presence of medicine found in Kit 8 she would have lacked post-operation medicine. “After the menstrual regulations services I was prescribed a few medicines which I could not buy due to poor financial condition,” she says. “But the hospital gave me a number of medicines that I could take.” And while Khatun had talked with women about various family planning methods, she didn’t feel she could talk with anyone aside from her husband about getting the procedure. “I feared they would treat me poorly (the hospital),” she says. But Kahtun says she found the hospital trustworthy and helpful, even when she was suffering complications such as mass bleeding. “I will be very cautious that I should not get pregnant again however in event if I get pregnant again then I will come to this hospital only,” she says.

| 08 February 2018
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”

| 15 February 2026
“My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself”
Menstrual regulation, the method of establishing non-pregnancy for a woman at risk of unintended pregnancy, has been a part of Bangladesh’s family planning program since 1979. It is allowed up to 10 –12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. Auliya Khatun, a mother of three children, was 40 years old when she found out that she had unintentionally become pregnant again. Khatun says she had heard about family planning services and menstrual regulation services available at the Upzila Health Complex from other women in her small village. She discussed the option of undergoing menstrual regulation with her husband. “My spouse was supportive and he gave me the freedom to come to this decision myself,” Khatun says. “If this service was not available then I would have carried on with the pregnancy. It would have been embarrassing, though,” she explains. “It is embarrassing to have another child at this age.” Khatun, who sometimes assists her husband with work in a local handloom, also cited the financial burden another child would have on her family. “We are facing financial difficulty so it is not possible to have another child.” Khatun says she only experienced mild gastric discomfort after the procedure but felt assured about her recovery due to being able to check-in with doctors at the local health centre. The access to the services and doctors, she says, was a major factor in a smooth and easy recovery. “Since this service was in a government facility I could prevail [through] this and survive,” she says. “It is an important service.”








